GRACE23
ACL23 - GRACE:Gradient-guided Controllable Retrieval for Augmenting Attribute-based Text Generation
Zhihua Wen, Zhiliang Tian, Zhen Huang, Yuxin Yang, Zexin Jian, Changjian Wang, Dongsheng Li
Abstract
Attribute-based generation methods are of growing significance in controlling the generation of large pre-trained language models (PLMs). Existing studies control the generation by (1) finetuning the model with attributes or (2) guiding the inference processing toward control signals while freezing the PLM. However, finetuning approaches infuse domain bias into generation, making it hard to generate out-of-domain texts. Besides, many methods guide the inference in its word-by-word generation, pushing the word probability to the target attributes, resulting in less fluent sentences. We argue that distilling controlling information from natural texts can produce fluent sentences while maintaining high controllability. In this paper, we propose GRAdient-guided Controllable rEtrieval (GRACE), a retrieval-augmented generation framework to facilitate the generation of fluent sentences with high attribute relevance. GRACE memorizes the semantic and attribute information from unlabeled corpora and applies a controllable retrieval to obtain desired information. For the generation, we design techniques to eliminate the domain bias from the retrieval results and integrate it into the generation model. Additionally, we propose a gradient-guided generation scheme that iteratively steers generation toward higher attribute relevance. Experimental results and quantities of examples verify the effectiveness of our method.
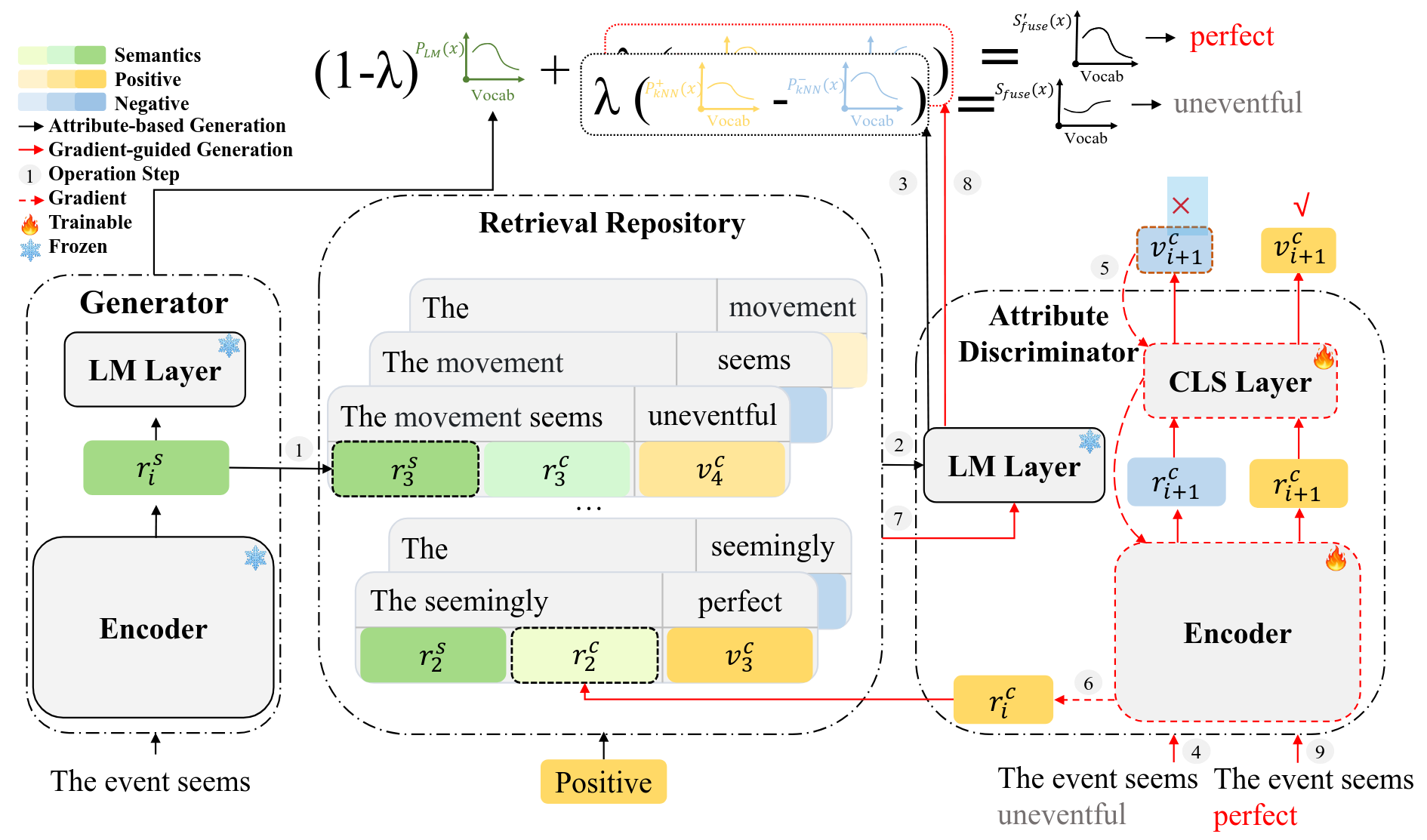
Our framework consists of three parts:
- Attribute Discriminator conducts attribute classification with a discriminator $D$ to evaluate if a given context satisfies the target attribute
- Retrieval Repository builds a repository $R$ with unlabeled corpora, which carries a mapping of a context $X_n$ to its next word $x_{n+1}$. $R$ supports reading operations to provide information that is semantically similar to the query and related to the target attribute
- Generator generates a sentence based on a prefix with a $\text{PLM} G$. At each step, $G$ retrieves (read) information from $R$, reduces the effect of domain-specific vocabulary, and integrates it into a neural network model to generate the next word.